This tutorial explains how to import Cargo's sources from Subversion into your IDE (Eclipse and IntelliJ IDEA are covered).
- Start by checking out the Cargo sources from Subversion. - You can do that using the Subversion command line, TortoiseSVN (recommended for Windows users), Git command line or GUI-based tools or your IDE Subversion feature (for Eclipse you'll need the Subclipse plugin) or any subversion client tool.
- Install the latest version Maven2 Maven 3. Make sure it's installed properly by typing
mvn --version.
- Open a shell in the top level directory where you have checked out the Cargo sources (this directory should have a
build-toolssubdirectory in it and it should contain a pom.xml file).
For Eclipse users
- Type "
mvn eclipse:eclipse". This generates Eclipse files automatically. - Start Eclipse.Select "
- Go to Windows|Preferences|Java|Build Path|Classpath Variables and add a
M2_REPOvariable to point to your local Maven repository (usually in~user/.m2/repository). See also the documentation on the Maven Eclipse plugin. - Select Import|Existing Project into Workspace". Point it to the top level directory of the checked-out Cargo sources. You should see something similar to the following figure:
...
Note: Maven supports a nested directory structure whereas Eclipse currently only supports a flat structure. The Maven2 Maven Eclipse plugin creates an Eclipse project per Maven module (i.e. per directory containing a pom.xml file). This means that directories with no pom.xml will not be listed. This is a known issue with Eclipse and Maven. In the future the hope is that Eclipse will support nested project structure.
For IntelliJ IDEA users
- Type "
mvn idea:idea". This generates IDEA project files automatically. - Start IntelliJ IDEA.
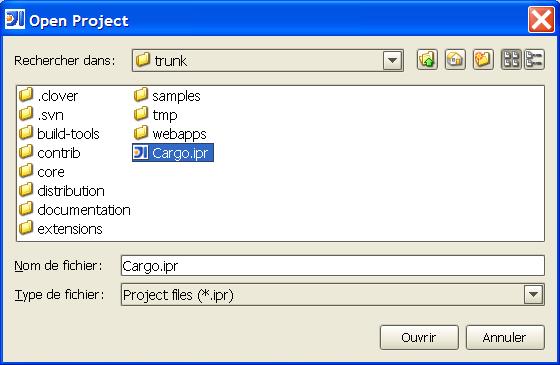
- Select " File|Open Project... " and select the Maven-generated project as shown in the following figure: